Adjustment Layers
The Adjustments tab of the Layers pane can be used to non-destructively adjust and add effects to images. Adjustment layers stack in the Layers pane, allowing individual layers to be revisited at any time and for adjustments to be made to each effect. Each adjustment layer includes a mask by default.
By saving an image with adjustment layers as an .gsd file, the file can be reopened and adjustments made for each effect at any time.
For best results, make all global adjustments prior to adding adjustment layers.
To add an Adjustment Layer:
With an image open, do one of the following:
- Select Layer | New Adjustment Layer from the menu.
- In the Layers pane, select the Adjustments tab, then click an adjustment layer icon.
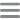
The adjustment layer is added above the image in the Layers pane. The adjustment layer settings appear at the bottom of the panel. Configure the settings as described below.
To apply an Adjustment Layer to a particular image:
If there are multiple images in the Layers pane, adjustment layers can be restricted to a specific image.
To apply an adjustment layer only to the closest image layer below it, enable the Clipping button.

|
Clipping off |

|
Clipping on |
Enable multiple clipping buttons to apply multiple adjustment layers to one particular image layer.
Adjustment Layers and Settings
|
Exposure |
Drag the slider to the right to increase exposure, or drag to the left to decrease exposure. |
|
Contrast |
Drag the slider to the right to increase contrast, or drag to the left to decrease contrast. |
- Use the buttons on the right of the Levels panel to select Luminance, Red, Green, or Blue as the channel to adjust.
- Use the arrows at the bottom of the panel to adjust the shadows, midtones, and highlights. Move the shadows arrow to define the blackest area of the image. Move the midtones arrow to define the midtone. Move the highlights arrow to define the whitest area of the image.
Use the buttons on the right of the Curves panel to select the RGB, Red, Green, or Blue color channel to adjust.
|
Brighten |
Drag the slider to increase the brightness of dark areas in your image. |
|
Darken |
Drag the slider to decrease the brightness of light areas in your image. |
|
Temperature |
Adjusts the warmth of the correction, from blue to yellow. |
|
Tint |
Adjusts the tint of the correction, from magenta to green. |
|
Vibrance |
Drag the slider to the right to increase vibrance, or to the left to decrease vibrance. Increasing vibrance does not affect skin tone in an image. This is unlike saturation, which intensifies all colors equally. |
|
Saturation |
Drag the slider to the right to increase saturation, or to the left to decrease saturation. |
|
Hue |
Adjusts the hue of the image. Drag the slider to the right to increase or drag to the left to decrease hue. |
|
Lightness |
Adjusts the image brightness. Drag the slider to the right to increase or drag to the left to decrease the image's brightness. |
|
Choose the Saturation, Hue, or Brightness tab and adjust colors individually by dragging the sliders. |
|
|
Vibrance |
Drag the slider to adjust the vibrance of the image without affecting skin tones. |
|
Saturation |
Adjusts from saturation to grayscale. |
|
Hue |
Changes the color's hue. |
|
Brightness |
Adjusts the light or dark tones in the image. |
Adjust the Red, Green, or Blue sliders to balance or heighten the RGB channels in the image.
- Select a color to add to your image.
- Use the Density slider to specify the strength of the added color.
|
Adjust the Red, Green, or Blue sliders to add color back into the black and white image. |
|
|
Brightness |
Adjusts the brightness of the colors in the image. |
The Negative adjustment layer creates a negative out of the image. There are no settings for this adjustment layer.
Select a photo effect from the drop-down menu to change the look and feel of your image.
Use the mouse wheel to quickly scroll through the photo effects.
![]() Skin Tune
Skin Tune
|
Smoothing |
Refines skin by suppressing texture detail. |
|
Glow |
Increases the brightness of skin while subtly smoothing. |
|
Radius |
Specifies the scale of the texture detail that is affected by the effect. A lower value enhances small details, while a large value enhances larger details. |
![]() Sharpen
Sharpen
|
Strength |
Specifies the strength of the sharpening applied by increasing contrast around edges. |
|
Radius |
Controls the number of pixels to adjust around each edge. Higher values increase the number of sharpened pixels and tend to bring out coarser detail, while lower values reduce the number of sharpened pixels and tend to bring out finer detail. |
|
Detail |
Suppresses the halo, (the light border that forms around edges with extreme sharpening), by reducing its intensity. The higher the value, the stronger the reduction. |
|
Threshold |
Specifies how different the pixel lightness values within an edge must be before the pixels within the edge are sharpened. Higher values sharpen only stronger edges but minimize the appearance of noise. Lower values sharpen both strong and weaker edges, but can increase the appearance of noise. We recommend you set the threshold to enhance edges while keeping background noise to a minimum. |
![]() Blur
Blur
|
Select the Gaussian or Directional button to select the type of blur. |
||
|
Gaussian |
Produces an even, smooth blur. |
|
|
Strength |
Specifies the strength of the blur. Move the slider to the right to intensify the effect. |
|
|
Directional |
Produces a blurring effect that gives the illusion of movement. |
|
|
Strength |
Specifies the strength of the blur. Move the slider to the right to intensify the effect. |
|
|
Angle |
Specifies the direction of the blur effect. |
|
![]() Noise Reduction
Noise Reduction
|
Luminance |
Removes the random variations of brightness in the noise. |
|
Strength |
Drag the slider to the right to control how aggressively to reduce noise. Prevent the loss of detail by balancing Luminance with Strength. |
|
Color |
Reduces the random variations of color in the noise. |
|
Tonal Range |
Tonal Range refers to a range of average brightness values in an image. For example, the tonal range of a photo taken in a dark cavern it would be low, whereas a sunny sky would be high. The Tonal Range slider increases in value from left to right, increasing from a low tonal range on the left to a high tonal range on the right. The Tonal Range slider is used to focus noise reduction to areas of the image that have a corresponding tonal range. For example, the left-most position would reduce the noise in a cavern more than a sky. Tonal Range only affects luminance noise reduction. |
|
Frequency Range |
The Frequency Range slider adjusts the noise pattern. High frequency noise looks like fine static while low frequency noise looks like coarse grain or "splotches". Move the Frequency Range slider to the left to limit noise reduction to high frequency noise. Frequency Range affects both luminance and color noise reduction. |
|
Highlights Hue |
Drag the slider to the right to select a highlight color. |
|
Highlights Saturation |
Drag the slider to the right to increase saturation of the specified color in the highlights of the image. |
|
Shadows Hue |
Drag the slider to the right to select a shadow color. |
|
Shadows Saturation |
Drag the slider to the right to increase saturation of the specified color in the shadows of the image. |
|
Balance |
Drag the slider to the right to emphasize the highlight color; drag the slider to the left to emphasize the shadow color. For example if the slider is set to the maximum at 50, then full emphasis is applied to the highlight color; if the slider is set to the minimum -50, then full emphasis is applied to the shadow color. |
![]() Clarity
Clarity
|
Clarity |
Drag the slider to the right to enhance texture in the image. Drag the slider to the left to smooth out texture in the image. |
|
Orton |
Drag the slider to enhance local contrast while subtly smoothing texture. |
|
Soft Light |
Drag the slider to increase brightness while subtly smoothing texture. |
|
Tonal Width |
Drag the slider to control the amount shadow and highlights are affected by the Clarity, Orton, and Soft Light sliders. Choose a value of 0 to restrict the adjustments to midtones. Choose a value of 100 to apply the adjustments equally in all tones. |
|
Radius |
Drag the slider to control the scale of the texture detail being affected. Choose a value of 0 to enhance small details, or a value of 100 to enhance larger details. |
|
Enhanced edge processing |
Select this checkbox to reduce the appearance of halos around edges with enhanced texture, and to minimize the softening of edges when texture is smoothed. |
![]() Dehaze
Dehaze
Drag the slider to adjust the strength of the contrast, detail, and color correction.
|
Shadows |
Specify the color to be added to the dark parts of the image. |
|
Highlights |
Specifies the color to be added to the light parts of the image. |
![]() Vignette
Vignette
|
Strength |
Specifies the size and intensity of the vignette. |
|
Distance |
Specifies the size of the clear area around the focal point in the portrait. Drag the slider to the left to reduce the size of the clear area. Drag the slider to the right to increase the size of the clear area. |
|
Shape |
Specifies the shape of the frame. |
See Applying a Posterize Effect.
Use the slider to select a brightness level. All pixels brighter than that brightness will become white, and every darker pixel will become black.
Select a Color LUT from the drop-down menu. Or click the Import LUTs button to import a new LUT.